Modes of heat transfer in packed beds
2025-08-10
In my previous article on the effective axial thermal conductivity in a packed bed, I grouped the main mechanisms of heat transfer into convection, conduction and radiation. A more detailed description of each heat transfer mechanism was provided by Yagi and Kunii in 1957:
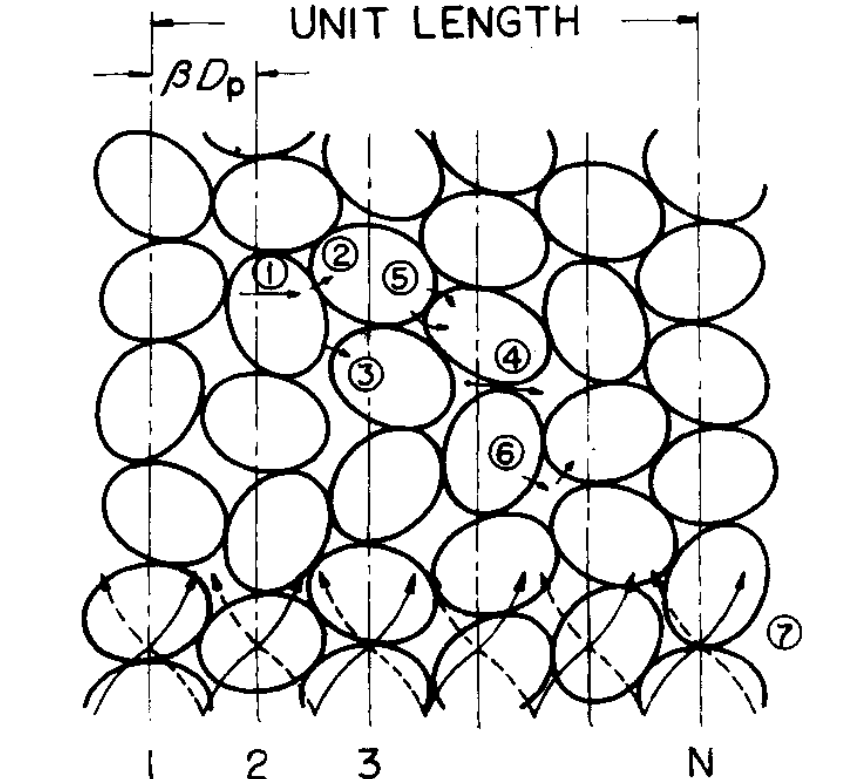
Where: (1): Thermal conduction through a solid; (2): Thermal conduction through the contact surfaces of two packings; (3): Radiant heat transfer between surfaces of two packings (in the case of gas); (4): Radiant heat transfer between neighbouring voids (in the case of gas); (5): Thermal conduction through the fluid film near the contact surface of two packings; (6): Heat transfer by convection, solid-fluid-solid; (7): Heat transfer by lateral mixing of fluid.
This description provided by Yagi and Kunii doesn't include the modes of heat transfer with the wall of a packed bed, which are included by Adeyanju and Manohar:
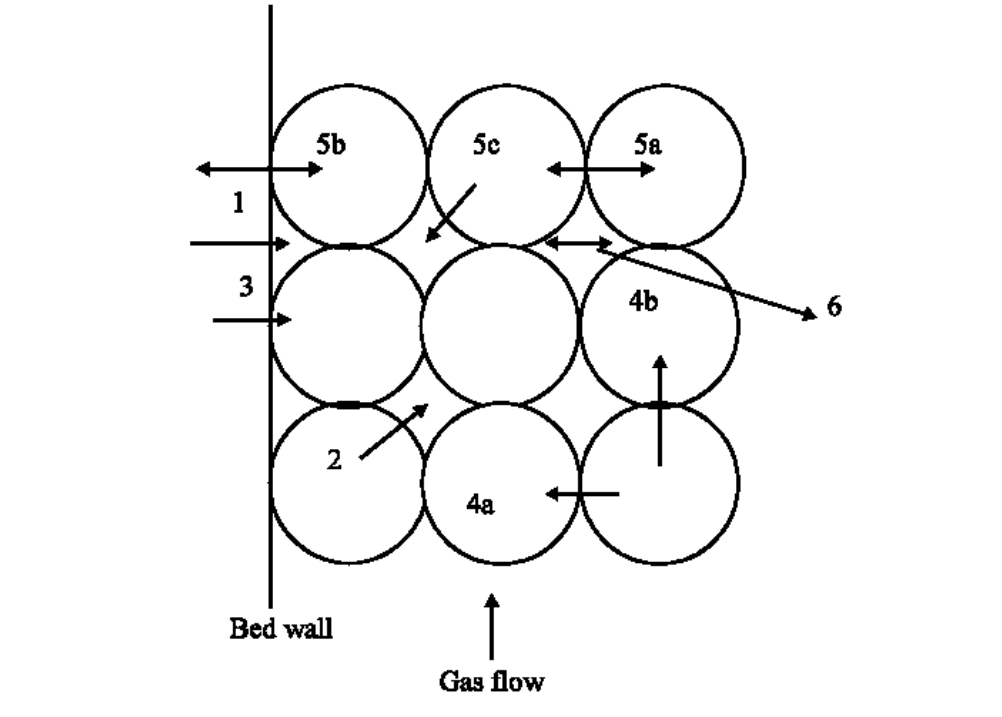
Where:
(1): Wall to fluid convection; (2): particle to fluid convection; (3): Wall to particle conduction; (4a): Radial particle to particle conduction; (4b): Axial particle to particle conduction; (5a): Radiant heat transfer between particles; (5b): Radiant heat transfer between wall and particles; (5c): Radiant heat transfer between fluid and particle; (6): Heat transfer by mixing of the fluid.
Comparing the two models, we see that mode (1) from Yagi and Kunii is missing in the above model, and particle-particle conduction has been separated into a radial (4a) and axial (4b). Additionally, mode (5) from Yagi and Kunii is omitted. Mode (5) dominates at low Re numbers when the boundary layers surrounding the particle are thick, and as a result, almost all the heat flows through the fluid near the contact point between two solids. At large Re numbers, boundary layers are much thinner, and mode (7) tends to dominate.
I've attempted to compile a comprehensive list of each heat transfer mechanism, with the above two models in mind: (1a): Thermal conduction through solid; (1b): Thermal conduction through the contact surfaces of two packings; (1c): Thermal conduction through the contact surfaces of solid-wall; (1d): Thermal conduction through the fluid film near the contact surface of two packings; (2a): Radiant heat transfer between surfaces of two packings (in the case of gas); (2b): Radiant heat transfer between neighbouring voids (in the case of gas); (2c): Radiant heat transfer between wall and particles (in the case of gas); (3a): Heat transfer by convection, solid-fluid; (3b): Heat transfer by convection, wall-fluid; (4): Heat transfer by lateral mixing of fluid.
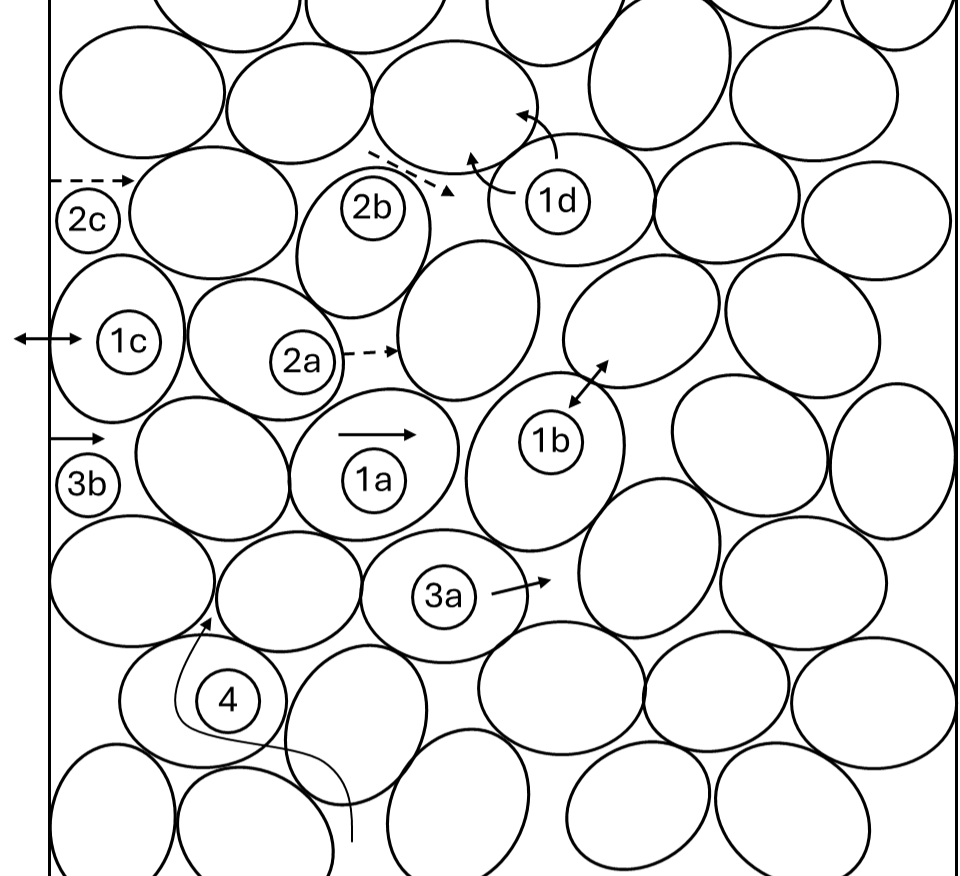
Where (1) groups conduction, (2) groups radiation, and (3) groups convection modes.